BERTopic v0.16 소개:
오늘은 핸즈온 LLM 책을 집필하고 계시고 BERTopic과 Keybert를 개발 하신 Maarten Grootendorst은 BERTopic의 최신 릴리스를 소개하며 토픽 모델링에 대한 포괄적인 도구로 발전시키는 노력을 소개합니다. 주요 내용으로는 제로샷 토픽 모델링, 사전 훈련된 모델 병합 및 대규모 언어 모델에 대한 강화된 지원과 같은 주요 기능을 다룰 것입니다.
자세한 내용은 유튜브 영상속에 있습니다.
https://youtu.be/Ba-a3EJh_Pw?si=kJVDh7paUXQXDBNy
BERTopic 개요:
BERTopic은 사용자 정의 토픽 모델을 구축하기 위한 모듈화된 프레임워크입니다.
기본 사용법은 임베딩을 생성하고, UMAP을 사용하여 5차원으로 축소하며 의미론적 유사성을 위한 클러스터링을 수행하고, 다양한 가중치 체계를 사용하여 토픽을 추출하는 것을 포함합니다.
다양한 모델을 사용할 수 있도록 함으로써 토픽 모델링을 만들 수 있습니다.
제로샷 토픽 모델링:
사용자가 토픽 레이블을 생성하여 사전 정의된 토픽을 찾을 수 있는 유연한 기술을 소개합니다.
코사인 유사성을 사용하여 토픽을 문서에 매핑하여 수동 BERTopic 모델과 일치하지 않는 문서에 대한 새로운 모델을 만듭니다.
정의된 및 새로운 토픽을 모두 발견할 수 있도록 하여 토픽 할당에 대한 유연한 접근을 제공합니다.

from datasets import load_dataset
from bertopic import BERTopic
from bertopic.representation import KeyBERTInspired
# We select a subsample of 5000 abstracts from ArXiv
dataset = load_dataset("CShorten/ML-ArXiv-Papers")["train"]
docs = dataset["abstract"][:5_000]
# We define a number of topics that we know are in the documents
zeroshot_topic_list = ["Clustering", "Topic Modeling", "Large Language Models"]
# We fit our model using the zero-shot topics
# and we define a minimum similarity. For each document,
# if the similarity does not exceed that value, it will be used
# for clustering instead.
topic_model = BERTopic(
embedding_model="thenlper/gte-small",
min_topic_size=15,
zeroshot_topic_list=zeroshot_topic_list,
zeroshot_min_similarity=.85,
representation_model=KeyBERTInspired()
)
topics, probs = topic_model.fit_transform(docs)
topic_model.get_topic_info()
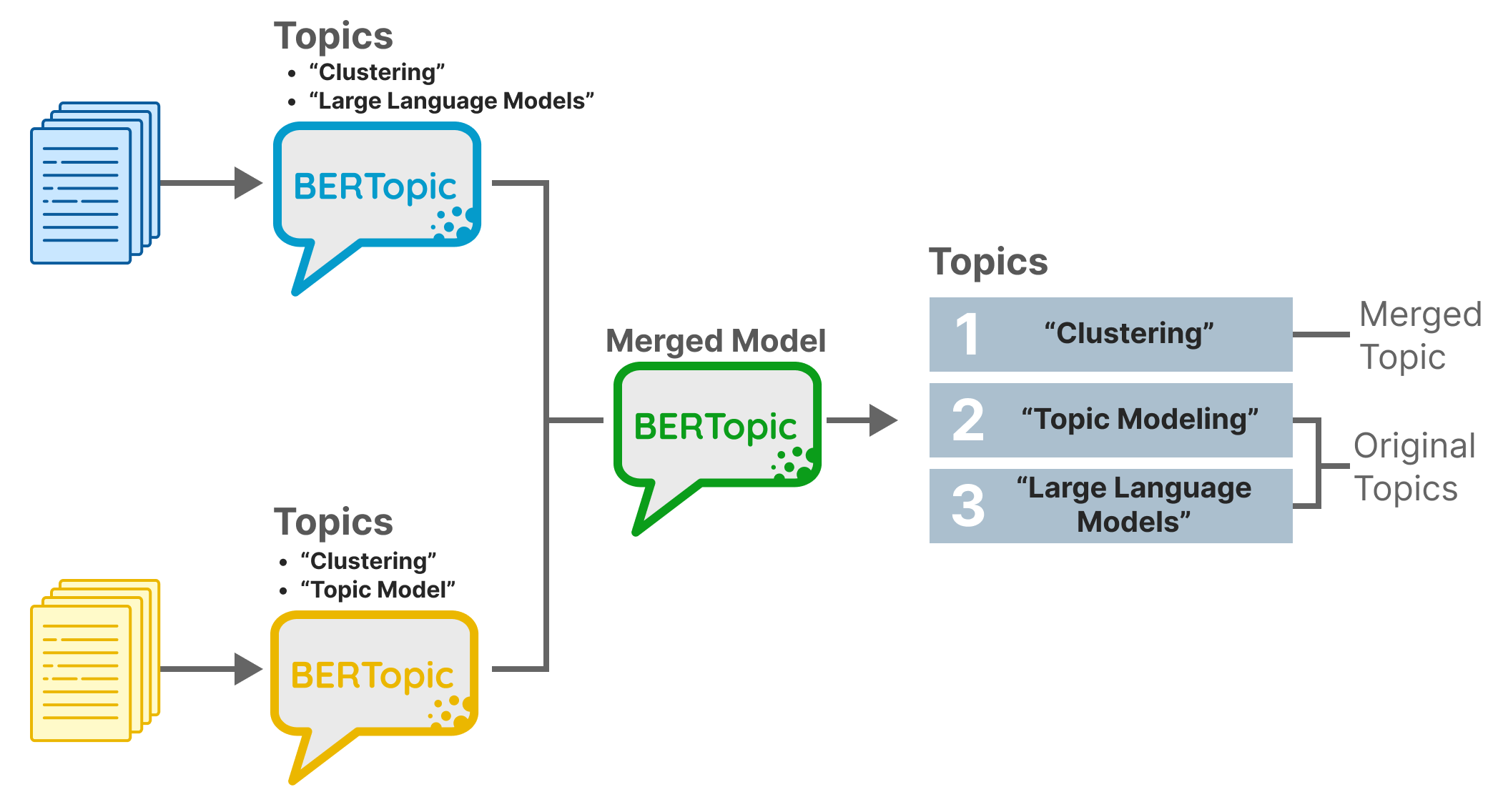
모델 병합:
토픽 유사성을 기반으로 두 BERTopic 모델을 병합하는 기능을 소개합니다.
연합 학습 및 점진적 학습과 같은 응용 프로그램에 유용하며 다양한 출처 또는 업데이트에서 지능적으로 모델을 결합할 수 있습니다.
모델을 무작위로 쌓지 않고 똑똑하게 병합하여 향상된 표현을 촉진합니다.
from bertopic import BERTopic
from bertopic.representation import KeyBERTInspired
from datasets import load_dataset
# Prepare documents
all_docs = load_dataset("CShorten/ML-ArXiv-Papers")["train"]["abstract"][:20_000]
doc_chunks = [all_docs[i:i+5000] for i in range(0, len(all_docs), 5000)]
# Base Model
representation_model = KeyBERTInspired()
base_model = BERTopic(representation_model=representation_model, min_topic_size=15).fit(doc_chunks[0])
# Iteratively add small and newly trained models
for docs in doc_chunks[1:]:
new_model = BERTopic(representation_model=representation_model, min_topic_size=15).fit(docs)
updated_model = BERTopic.merge_models([base_model, new_model])
# Let's print the newly discover topics
nr_new_topics = len(set(updated_model.topics_)) - len(set(base_model.topics_))
new_topics = list(updated_model.topic_labels_.values())[-nr_new_topics:]
print("The following topics are newly found:")
print(f"{new_topics}\n")
# Update the base model
base_model = updated_model
대규모 언어 모델 지원의 확대:
대형 문서를 처리하는 데 사용되는 문서 절단 기능을 소개합니다.
Lama CPP Python을 사용하여 대형 언어 모델을로드하고 사용하는 기능을 강화합니다.
다양한 문서 길이를 처리하고 대형 언어 모델을보다 무결하게 통합하는 데 BERTopic의 기능을 향상시킵니다.

from bertopic import BERTopic
from bertopic.representation import LlamaCPP
# Use llama.cpp to load in a 4-bit quantized version of Zephyr 7B Alpha
# and truncate each document to 50 words
representation_model = LlamaCPP(
"zephyr-7b-alpha.Q4_K_M.gguf",
tokenizer="vectorizer",
doc_length=50
)
# Create our BERTopic model
topic_model = BERTopic(representation_model=representation_model, min_topic_size=20, verbose=True).fit(docs)참조자료
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ba-a3EJh_Pw&ab_channel=MaartenGrootendorst
'코딩 > LLM' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Efficient Training of Language Models to Fill in the Middle 언어 모델 효과적인 훈련을 위한 중간 부분 채우기 | 논문 리뷰 영상 감상 (0) | 2024.01.18 |
|---|---|
| tiktoken 및 cl100k_base을 오프라인에서 사용후기 (0) | 2024.01.15 |
| Gemini Pro API 사용해보기 (Python, Langchain) (1) | 2023.12.18 |
| 라마 인덱스와 랭체인 비교 (0) | 2023.11.01 |
| 벡터 데이터베이스와 벡터 인덱스 Faiss (1) | 2023.10.29 |

